Origin of the Universe
One of the most difficult problems facing
scientists in the 20th century was to explain how the Universe was
created. The Universe is changing, but from what and to what? The Steady State
theory suggested that the Universe had no beginning or end. The alternative,
and now generally accepted, theory is the Big Bang. It proposes that the
Universe was created in an explosion 15 billion years ago. From very small and
simple beginnings it has grown vast and complex.
Steady State Theory
In the late 1940s and the 1950s, the Steady State theory was as popular
as the Big Bang theory. It proposed that the Universe looked the same at any
place and at any time. Although expanding, it would stay unchanged and in
perfect balance. Material was being continuously created to keep the density of
the Universe constant. As scientists found proof for the Big Bang, the Steady
State theory was largely abandoned.
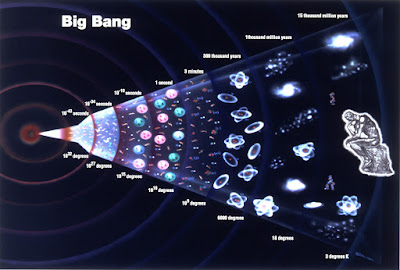
Big Bang Theory
All matter and time was created in
the Big Bang. The explosion started pushing everything away and the Universe
has been expanding ever since, and as the Universe expanded, the temperature
dropped. A fraction of a second after the explosion, the first tiny particles began
to form. By the time the Universe was three minutes old it consisted of 75 per cent
hydrogen and 25 per cent helium. Everything that exists now- galaxies, stars,
Earth, and humans- was created from these elements. In 1931, a Belgian
cosmologist Georges Lemaltre (1894 - 1966) was the first to put forward the
theory that the Universe started from a dense, single unit of material in a big
explosion. The name Big Bang followed in 1950, introduced by Fred Hoyle, a
British astronomer and supporter of the Steady State theory.
Expanding Universe:
In the 1920’s analyzing
starlight from galaxies showed that the galaxies are moving away from Earth.
This is true of galaxies in every direction from Earth. Over time, the Universe
is becoming larger and less dense. The idea that the Universe started in an
explosion from a single point grew out of observations that the Universe is
expanding.
The heat produced by the Big Bang has been cooling
ever since. It now has a temperature of -270°C (-454°F), detected as microwave
radiation from all over the sky.
Future of the Universe
Nobody knows for certain what
is going to happen to the Universe. At present, it is getting larger and less
dense. Most astronomers believe there will be a time when it stops expanding.
But there is disagreement about what happens then: will the Universe live on
for ever, wither and die, or start to contract?
The Universe may end in a Big Crunch if it starts to
contract until it is hot and dense once more. But even this may not mean the
end of the universe. The Big Crunch might be followed by another Big Bang
explosion, and the whole process could start over again.




No comments:
Post a Comment